Earthlings can rest easy: the predicted apocalypse set for 2032 has been called off.
The refined trajectory (in red) that 2024 YR4 may follow in 2032. It barely impacts Earth.
The European Space Agency (ESA) has effectively canceled the alert issued for December 24, 2032. Astronomers had predicted that on this date, Earth would encounter the rather substantial asteroid 2024 YR4, which was unexpectedly discovered at the end of last year. With a size ranging from 50 to 100 meters in diameter, it was argued that a collision with densely populated areas would be equivalent to a 30-megaton nuclear explosion. The asteroid even received the unofficial title of "city killer" - it truly has the potential to obliterate a major metropolis.
Researchers, who recently kept increasing the chances of a collision, have finally reduced them.
Last week, NASA assessed the likelihood of a catastrophe at 3.1 percent. Now, however, it has been lowered to 0.001 percent – according to ESA's forecasts. This means that the European Space Agency has essentially ruled out a collision. Earthlings can rest easy.
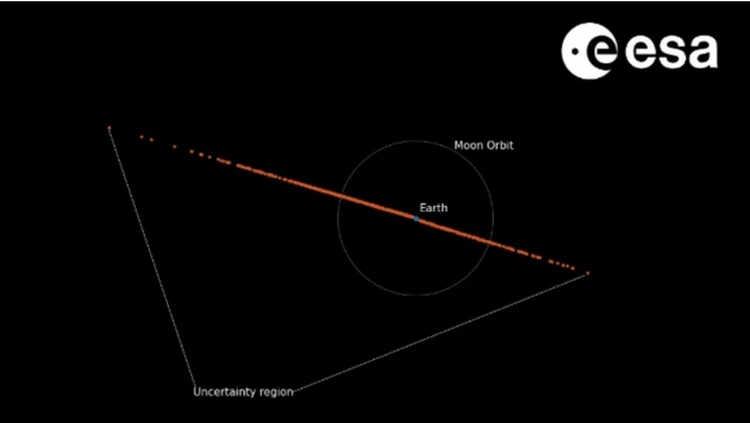
The probability zone for a collision that astronomers "drew" last week. It touched Earth.
These successive clarifications were made based on hundreds of observations using ground-based telescopes directed at the currently retreating asteroid.
There remains a possibility that 2024 YR4 could collide with the Moon. Experts estimate the odds of such an outcome at 1 in 333.
Further adjustments to the asteroid's orbit and size will be available after astronomers observe it with the James Webb Space Telescope. This is expected to happen between March and May of this year.
To learn about the chances of a larger celestial body – significantly bigger than this "small fry" 2024 YR4, perhaps one kilometer in diameter or even more – colliding with Earth, read our article.