Collagen-based cancer models from jellyfish and 4D heart imaging: Discover the most fascinating research and innovations by scientists in Rostov.
In 2024, scientists frequently shared their achievements. Photo: press service of RSMU.
In 2024, universities in the Rostov region continued to showcase their research and developments. "KP-Rostov-on-Don" compiled a list of the most intriguing projects. The authors believe that these innovations will enhance the diagnosis and treatment of serious diseases in the near future.
CANCER DIAGNOSIS USING NEURAL NETWORKS
Southern Federal University has developed a cancer diagnosis method utilizing artificial intelligence. Researchers trained a neural network based on a large dataset of histology results — specifically images. Now, the AI can identify colorectal tumors, segment, and classify cancer cells. The model can predict prognosis with an accuracy exceeding 96%.
— Based on this neural network, software has been created for the automatic diagnosis of types of colorectal cancer. This development could serve as an excellent aid for doctors in establishing a morphological diagnosis, — believes Elena Varlamova, an engineer at the "Microfluidic Technologies for Accelerated Material Synthesis" laboratory.
 0
0At SFedU, a method for cancer diagnosis using AI has been developed. Photo: Southern Federal University.
At SFedU, it is noted that currently, artificial intelligence can be used in medicine not as a decision-making tool, but as a confirmation of decisions made by human specialists. This method is associated with several unresolved issues, such as data standardization, data bias, and insufficient clinical research. Another challenge is the underrepresentation of certain population groups.
COLLAGEN FROM JELLYFISH FOR CANCER MODELING
Don State Technical University has created a three-dimensional model of breast cancer. Researchers developed it using a scaffold made from jellyfish collagen. Initially, they populated the scaffold with normal human connective tissue cells. Over five days, these cells grew and ultimately formed a tissue analogue. Researchers then implanted spheroids of breast cancer cells into this structure, thereby recreating the process of tumor cell dissemination — their transfer through blood and lymph flow.
 1
1Photo: Don State Technical University.
— Today, models consisting of tumor and normal cells from specific patients, grown on three-dimensional scaffolds, represent the most promising experimental model for studying various types of malignant neoplasms and targeted drug therapy selection, significantly improving treatment efficacy, — the university stated.
The university also reminded that they can create products with various types of jellyfish collagen, including gel collagen, sterile collagen solutions, and collagen powders.
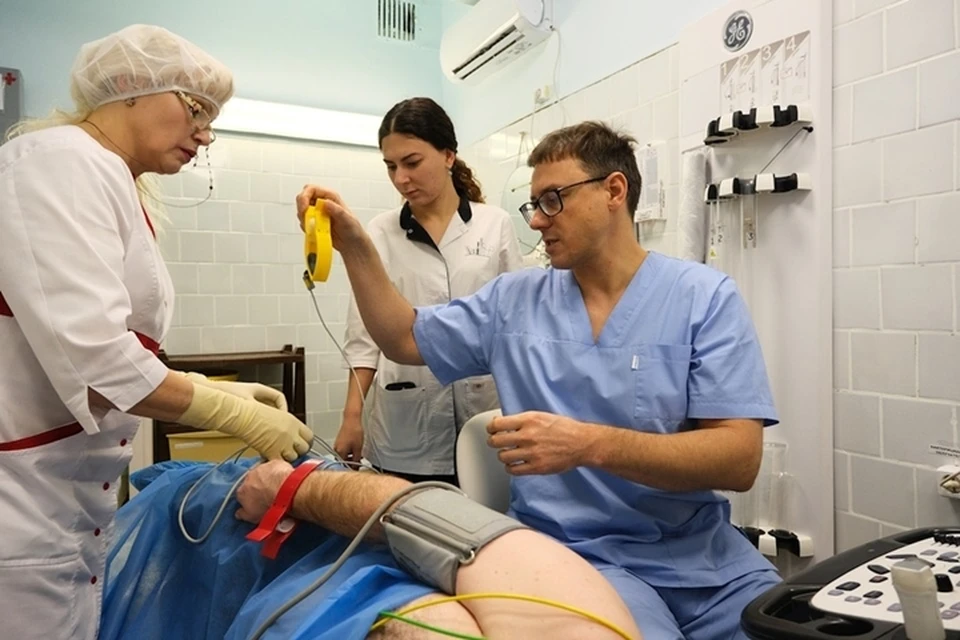
HEART RESEARCH IN 4D MODE
Rostov State Medical University has begun performing transesophageal echocardiography in 4D mode. Head of the ultrasound diagnostics department, Maxim Morgunov, explains that with this method, the ultrasound doctor can obtain a model of the organ with stereo visualization.
— The cardiac surgeon wears stereo glasses in our office and examines the image of what the heart looks like from the inside. Without opening the chest, he knows in advance what to expect, allowing him to choose the correct approach for the upcoming surgery, — says Maxim Morgunov.
 2
2Standard ultrasound only shows part of the heart's function, while the new 4D model displays the entire organ's operation. Photo: press service of RSMU.
Thus, doctors created such a model for a woman with a heart defect — interatrial septal defect, or simply put, perforation. Standard ultrasound does not reveal the shape of this opening. Only with this information can the cardiac surgeon determine how to place a patch, whether it is possible to operate through a vessel without opening the chest and stopping the heart.
READ ALSO
Rostov scientists peered inside the heart using a 4D model
In Rostov, scientists developed a methodology for diagnosing hidden heart dysfunctions. (Details)